

The functions of vital organs meet the following requirements (no blood components, cell growth factors and other corrective treatment drugs are allowed within 14 days before the first administration):.Newly diagnosed patients who have not received targeted therapy or immunotherapy in the past.BCLC-C stage accompanied by tumor thrombosis-associated portal hypertension.Clinically diagnosed or pathologically confirmed hepatocellular carcinoma, at least one measurable focus without local treatment (according to mRECIST requirements, the measurable focus spiral CT scan length ≥ 10 mm or enlargement Short diameter of lymph node ≥15 mm).≥18 and ≤ 75 years old, both male and female.The patient voluntarily joined the study and signed an informed consent form.Why Should I Register and Submit Results?.A pilot study of central venous catheter survival in cancer patients using low-molecular-weight heparin (dalteparin) and warfarin without catheter removal for the treatment of upper extremity deep vein thrombosis (the catheter study) JTH. National Partnership for Maternal Safety: Consensus bundle on venous thromboembolism. ↑ Diagnosis and Treatment of Lower Extremity Venous Thromboembolism: A Review.Superficial Venous thrombosis:disease progression and evolving treatment approaches. How I treat isolated distal deep vein thrombosis (IDDVT). Clinical practice Deep-vein thrombosis of the upper extremities. Focus on: Emergency Ultrasound For Deep Vein Thrombosis. Does this patient have deep vein thrombosis? JAMA. Utility of the lower extremity venous ultrasound in the diagnosis and exclusion of pulmonary embolism in outpatients. Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism by multidetector CT alone or combined with venous ultrasonography of the leg: a randomised non-inferiority trial. REBEL EM - Should I Stay or Should I Go: Outpatient Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism.Check creatinine on all patients prior to initiation.Check PTT after 6hr adjust infusion to maintain PTT at 1.5-2.5x control.Unfractionated Heparin 80 units/kg bolus.Then 5mg PO BID daily (duration depending on risk factors).

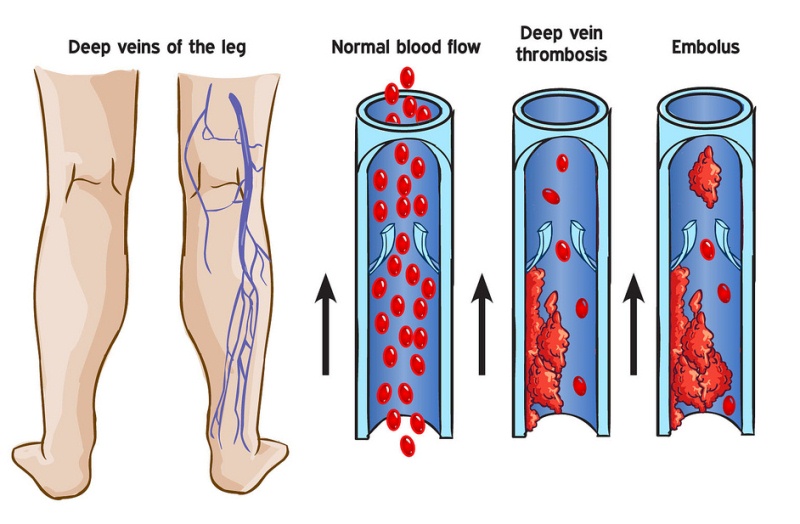

Unilateral calf swelling >3cm below tibial tuberosity (1pt).Active cancer (3 days because of symptoms within 4 weeks (1pt).Modified Wells ScoreĬan be applied for patients whose clinical presentation is concerning for a DVT in order to risk stratify. Risk stratification for further testing indicated using, e.g.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
